Break-throughs in visible circadian pattern disturbance.
- Research initiated 15 years ago at University of Western Australia to test the theory that mental state is linked to autonomic nervous system (ANS), circadian and sleep disturbance.
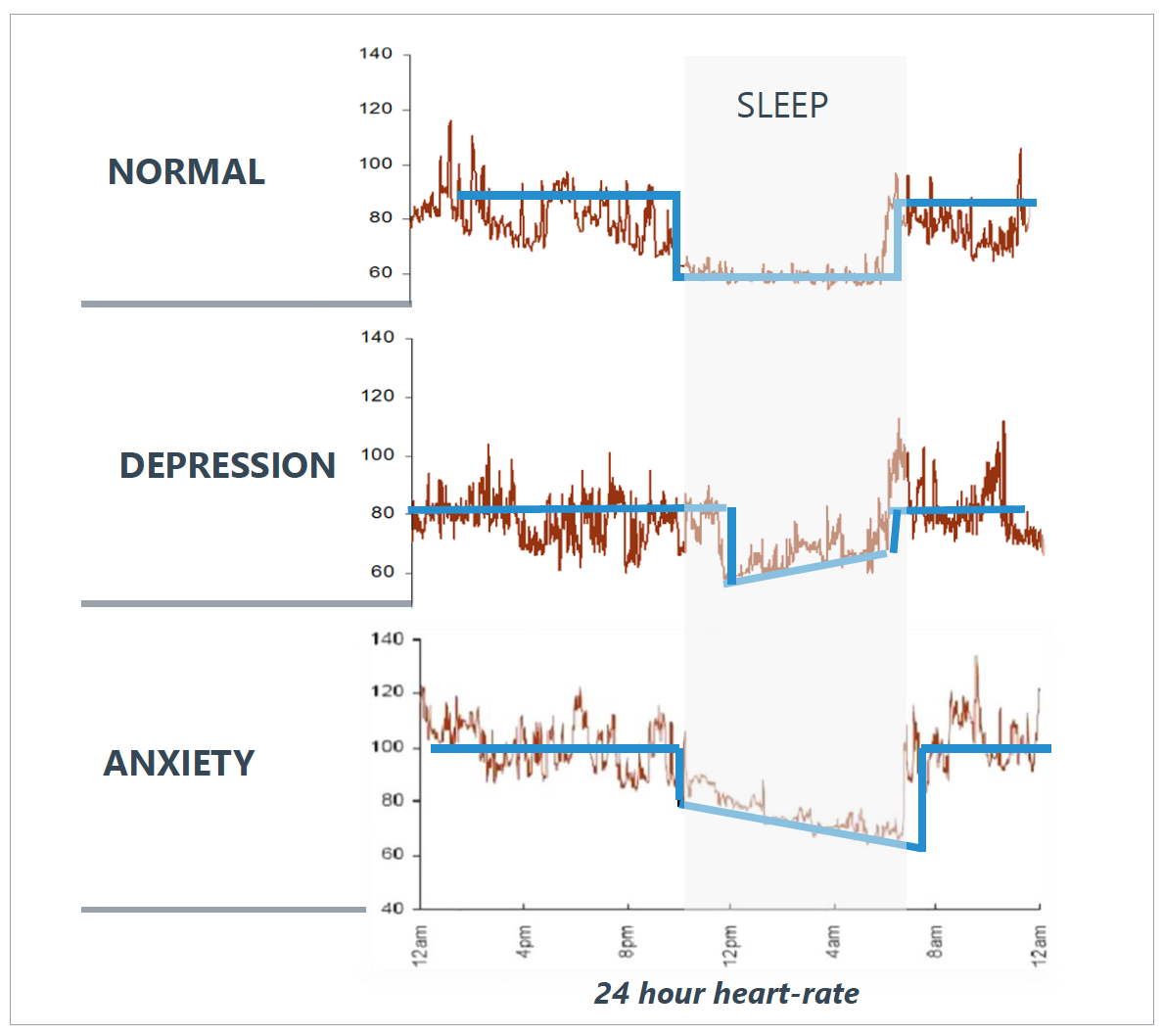
- Morphological analysis of circadian heart rate waveforms (CHR) gives objective indications of “core” physiological differences between different forms of mental Illness such as anxiety and depression.
- All serious mental illness (SMI) are associated with ANS and wider neuro endocrine dysregulation (especially affective disorders) and abnormalities in circadian regulation.
- Evidence of the state-dependent relationship between psychiatric status and CHR has come from serial monitoring of patients undergoing treatment – from individuals monitored days, weeks, months and years apart.
Looking at Mental Health, Objectively
Medibio technology summary
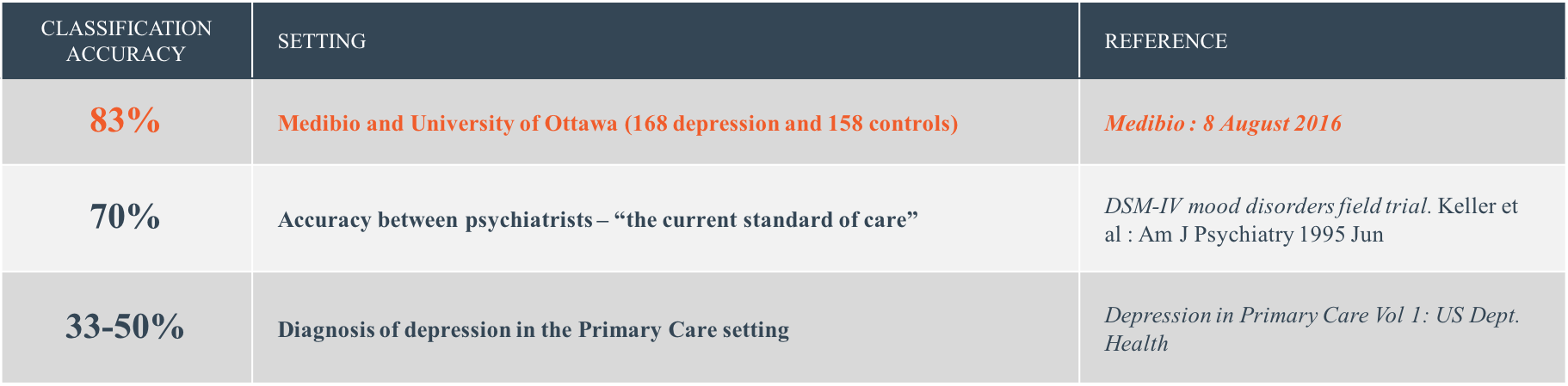
- Medibio’s technology has the potential to be the world’s first FDA approved objective measurement monitoring solution for mental illness.
- This patented innovative unique technology is non-intrusive, quick, objective, decisive and will revolutionise the diagnosis and treatment of mental health.
- Over 15 years of research into the relationship between the autonomic nervous system, psychological state and heart rate activity.
- Depression is estimated to cost US economy US$210 billion a year with the cost in Australia estimated at $12.6 billion annually.
- Currently rolling out our Corporate Stress Product with Wellness Channel partners.
“We will no longer endorse DSM5, as it has fundamental flaws and we are actively seeking a diagnostic system that is evidence based. We need a quantitative method for diagnosing depression. It is critical to realize that we cannot succeed if we use DSM categories as the gold standard.”
U.S. National Institute of Mental Health May 2013
* The relationship between psychiatric illness and the circadian pattern of heart rate. Hans G . Stampfer, Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1998; 32:187-198.


